STAC Catalogs¶
What Are They?¶
- Oftentimes raw data is not ready for analysis and requires pre-processing and the installation of a significant number of software packages (Fergason et al., 2021)
- allows for creation of metadata to make datasets indexable and discoverable (The STAC Specification, n.d.)
- promotes reproducibility, open data, and open science
- STAC specification means that these large datasets can be used on the cloud as opposed to being downloaded locally, shortens run time and improves ease of use

Figure credit: STAC Specification official logo from the STAC Index Site
Structure¶
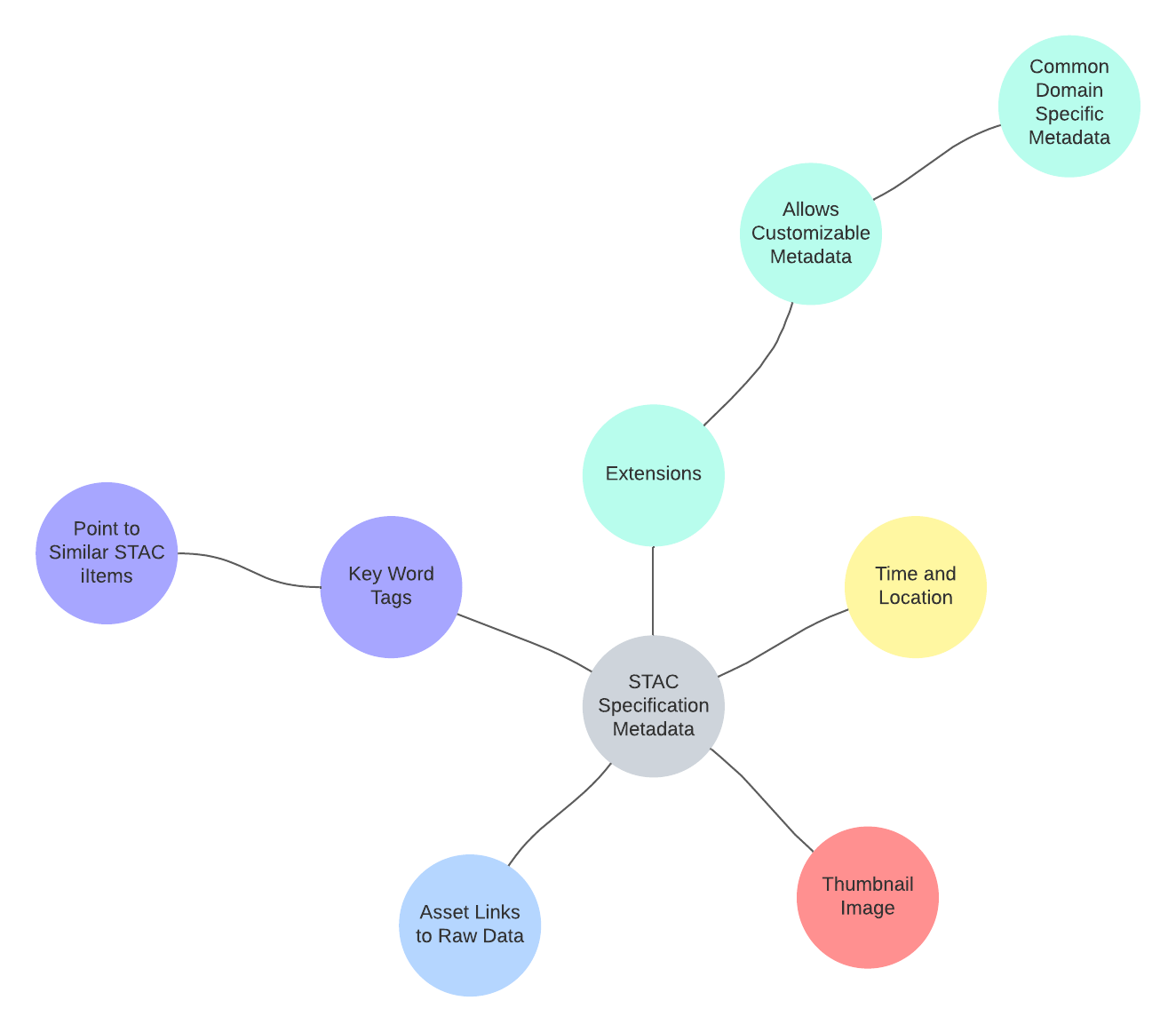
- composed of spatio-temporal assets- a piece of planetary data collected at a specific time with a specific location (The STAC Specification, n.d.)
- STAC specification designates inclusion of metadata on time and location of data, thumbnail for searching and discovery, applicable links to raw data, key words to describe relationship of data and point to similar spatio-temporal assets (The STAC Specification, n.d.)
- Users can further customize this metadata
- Spatio-temporal assets are a type of Javascript Object Notation (JSON) File
- JSON files are a data interchange format that allow datasets to be displayed in a text based format (The STAC Specification, n.d.)
How Are They Used?¶
- used to index data, making it searchable and discoverable
- data standard for formatting and creating metadata for geospatial data
- promotes open data and reproducibility
- allows data to be shared, understood, and discovered
- used for geospatial data about the Earth; however can also be used for planetary data (Fergason et al., 2021)
- Can be viewed as a webpage using a STAC Browser
Use in Google's Earth Engine¶
- The GEE Public Data Catalog can be viewed as a STAC catalog, STAC browser, or HTML version
- allows searchability, discovery, and improves user functionality